Start Programming
View or download the code for this chapter on GitHub:
github.com/nousbase-edu-codes/First_Steps_in_Python
- Programming = telling a machine exactly what to do, step by step
- Programming language = the language we use to talk to machines
- Variables = names or labels of boxes that store values
- Variables are of different type like int (integer), float, str (string)
- Expression = something that produces value
- Functions = actions we perform
- Python lets us write instructions in a very human-friendly way
Note: Writing a program is just like writing a recipe!
What is Programming?
Programming is instructing a machine to perform a task.
In simple words, programming is telling a computer exactly what to do, step by step.
At Café, you say: A sandwich, please.
A human understands this instantly.
But notice what is hidden inside that sentence:
- Take bread-
- Prepare stuffing
- Put stuffing between bread
- Place sandwich on plate
- Serve it
This single sentence abstracts many steps.
For a human, a simple sentence A sandwich, please is enough.
Machines are different. They are incredibly fast, but they are not "smart" in the human sense.
For machine, you will need to instruct it step-by-step, just like above.
And the good news is: once you give them clear steps, they never get tired or bored.
That is programming: Breaking a big idea into small steps the computer definitely understands.
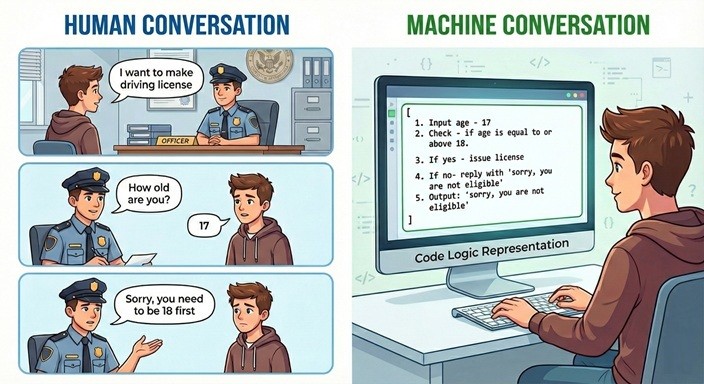
|
On the left side, a human conversation is happening. In the officer’s mind, many steps are abstracted:
Humans are good at this kind of abstraction. |
On the right side, this is how computer systems work, guided by step-by-step instructions. The instructions are:
This is programming.
We are going to learn how to give these step-by-step instructions, |
What is Programming Language?
If programming is the act of giving instructions, a Programming Language is the tool we use to write them.
Python is such a language. It has specific keywords (vocabulary) and syntax (grammar rules).
- You now understand what programming is.
- You learned how to convert human thinking into computer steps.
- This skill matters more than any programming language.
How do we instruct computers (how do we program?)
Let’s write our first program:
Write A Program To Know About “Functions”
Program 1.1: Display a message “Hi! I am Python”
Visit colab or
Run the program! You can see the output.
Congratulations!! Task 1.1 done!
print ( ) is a function.
Functions are actions we perform.
Processes we do in program like, Print, ask input etc. are functions.
By rules of the language, functions are followed by parenthesis, that is, ( ). Inside those parentheses, we provide some values. Function basically processes those values.
In this case, we provide “Hi! I am Python” as value to function. This value we provide to function is argument.
Write A Program To Know About “Variables”
Program 1.2: Say “Hello” to user with his/her name. e.g. Hello John
Now, in order to greet the user with his/her name, we need to know the user’s name.
How to know it? Simply, by asking the user!
So, we have 2 steps to solve the problem.
- Ask user his/her name.
- Display the message of greeting.
Step 1: Take user’s name. For this, we use input( ) function.
It pauses the program and waits for user input.

Now, you can enter your name here. But to display the name with greeting, we will need print( ) function.
How to tell the print( ) function your name?
For this, we use Variable.
Variable stores value. It is like a named box storing a value.
Think of it as a named box where the computer keeps something for later use.
Example:
age = 10
Step 2: Store name entered by user in variable.
This process assigns value entered by user to the variable name.
Step 3: Functions accept values stored in variables.
So, we pass variable name to print function.
print(name)
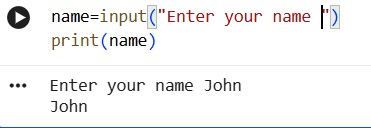
This is fine, but we want to add greeting too!
print( ) function accepts multiple arguments. So, we can simply add greeting line and name too.
print("Hello", name)
and you are done!
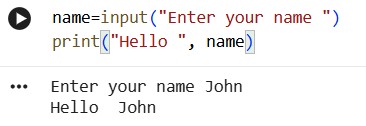
Progress Unlocked
- You can now take input, store it, and use it.
- You know what are functions and how to “call” them.
- You know what are variables.
1. The text we want to display exact → included in quotes.
2. Variable name → we want to display value stored in it → NOT included in quotes.
We will see more about this further.
Naming the variable.
You can use almost anything as variable name, but beware of two points below.
- Good practice is, name of variable should represent what the value is about. For example, variable name age clearly indicates that value it holds is age of someone.
- Also remember, we have said, language has rules.
There are certain rules for naming the variable.
- Variable name must start with a letter or underscore
- Cannot start with a number
Write A Program To Know About “Expressions”
Program 1.3: Take 2 numbers from user and display sum of the numbers
Steps:
1. Ask user to input 2 numbers
2. Store values in variables
3. Add the numbers
4. Display the result
Let’s start our program.
second_number = input("Enter second number")
How to add 2 numbers? How to print?
Mathematical operations are simple. We use operators like we use in maths.
| Operator | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | a + b |
| - | Subtraction | a - b |
| * | Multiplication | a * b |
| / | Division | a / b |
| % | Modulus (gives remainder) | a % b [7 % 3 gives 1] |
| // | Floor division | a // b [7 // 3 gives 2] |
And to make printing easy, we simply use variable to store the result.
second_number = input("Enter second number")
result = first_number + second_number
print(result)
Let’s run the program!
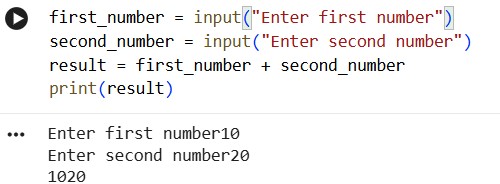
Oops!
We wanted 30 as result. Why did we get 1020?
It is because whatever input function returns is treated as text.
We need to understand data types of variables to understand in detail.
Variables and Data Types
Now, we have seen variable stores value.
These values are of different types. Type of variable values is very important concept.
Common basic types are:
- int: integer. e.g. 5, -10
- float: decimal number. e.g. 3.5, 7.34
- str: string in quotes. e.g. "Hello", "9"
- bool: True / False
Type Conversion
To perform mathematical operations, input values must be converted to numeric type using int( ).
second_number = int(input("Enter second number"))
result = first_number + second_number
print(result)
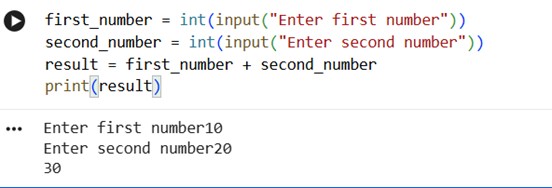
And we are done with the program 1.3!
Progress Unlocked
- You know about data types
- You can convert data types from one to another
- You can write expressions
- You can perform mathematical operations
Program 1.4: Calculate the age of user
Read the program below and try to understand what’s going on
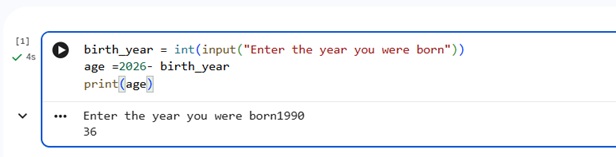
Concepts we learnt revisited:
- birth_year and age: Variables with data type int
- input("Enter the year you were born") and print(age): functions
- "Enter the year you were born" and age: arguments for functions input( ) and print( )
- 2025 - birth_year : Expression
- int( ) : Type conversion
1-Minute Challenge
Modify the program to print:
No hints. Try it yourself.
